The financial services industry is undergoing a revolutionary transformation, one that touches virtually every aspect of how we manage, invest, and think about money. At the heart of this revolution lies Fin Tech, a powerful convergence of finance and technology that is reshaping the economic landscape in ways that would have seemed impossible just a decade ago. From mobile payment apps that let us split restaurant bills instantly to sophisticated algorithms that provide personalized investment advice, Fin Tech is fundamentally changing the relationship between consumers and their finances.
Understanding the Fin Tech Revolution
Financial technology, commonly abbreviated as Fin Tech, represents the integration of cutting-edge technology into offerings by financial services companies to improve their use and delivery to consumers. This broad definition encompasses everything from mobile banking applications and cryptocurrency platforms to insurance technology and peer-to-peer lending services. What makes this transformation particularly significant is not just the technological innovation itself, but how it democratizes access to financial services that were once the exclusive domain of wealthy individuals and large institutions.
Fin Tech emergence of Fin Tech can be traced back to the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, when trust in traditional banking institutions reached historic lows. Entrepreneurs and technologists saw an opportunity to reimagine financial services from the ground up, leveraging smartphones, cloud computing, and data analytics to create more accessible, transparent, and user-friendly alternatives. Today, the global Fin Tech market is valued at hundreds of billions of dollars and continues to grow at an exponential rate, attracting massive venture capital investment and disrupting established financial institutions across every continent.
Mobile Payments and Digital Wallets: Money in Your Pocket
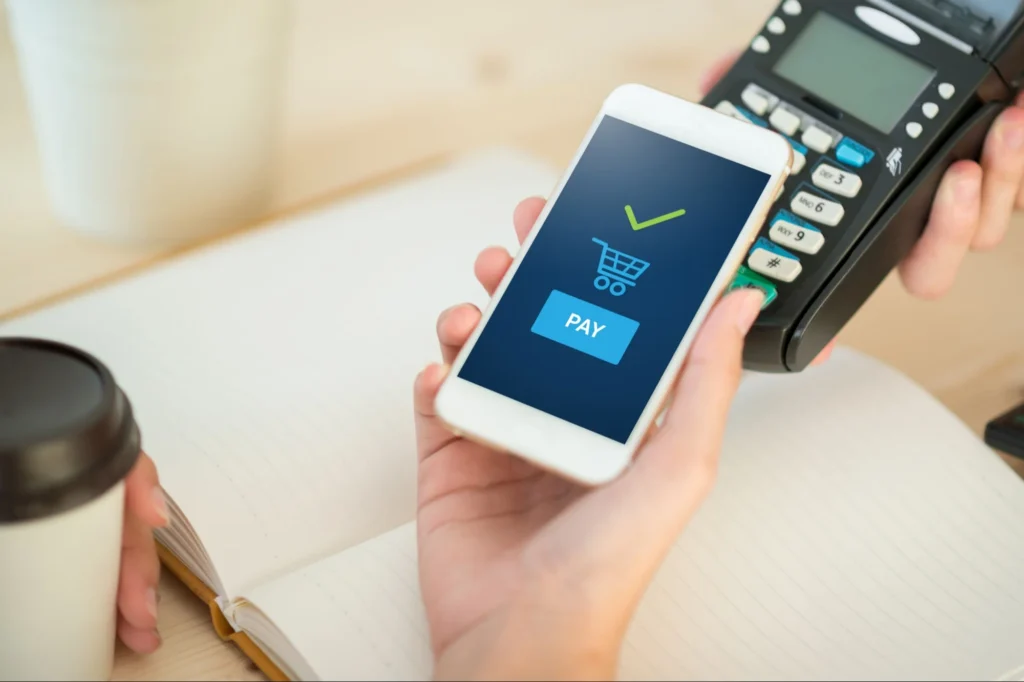

Perhaps the most visible manifestation of Fin Tech in our daily lives is the explosion of mobile payment platforms and digital wallets. Services like Apple Pay, Google Pay, Samsung Pay, and dedicated payment apps like Venmo, Cash App, and PayPal have transformed smartphones into powerful financial tools. These platforms allow users to make purchases, transfer money, and manage their finances without ever touching physical currency or plastic cards.
Fin Tech convenience factor cannot be overstated. Instead of fumbling for cash or cards at checkout, consumers can simply tap their phones to complete transactions in seconds. Beyond retail purchases, peer-to-peer payment applications have revolutionized how people handle everyday financial interactions, from splitting dinner bills to paying rent to sending money across international borders. What once required bank visits, wire transfer fees, and days of processing time can now be accomplished in moments with minimal or no fees.
Fin Tech security advantages of these platforms are equally impressive. Digital wallets employ tokenization, which replaces sensitive card information with unique digital identifiers, making transactions more secure than traditional card swipes. Biometric authentication through fingerprint or facial recognition adds another layer of protection that physical cards simply cannot match. For merchants, these technologies reduce the risk of handling cash and lower the costs associated with processing traditional card payments.
Banking Without Branches: The Rise of Digital-First Financial Institutions
Traditional banking required physical branches, banker’s hours, and often frustrating bureaucratic processes. Fin Tech has shattered these constraints by creating entirely digital banking experiences that operate 24/7 and can be accessed from anywhere in the world. Neobanks and digital-only financial institutions like Chime, N26, Revolut, and dozens of others have attracted millions of customers by offering streamlined account opening, no monthly fees, higher interest rates on savings, and intuitive mobile interfaces.
Fin Tech digital banks leverage technology to eliminate the overhead costs associated with maintaining physical branches, allowing them to pass those savings on to customers in the form of better rates and lower fees. Account opening that once required in-person visits and mountains of paperwork can now be completed in minutes through a smartphone app, with identity verification handled through document scanning and facial recognition technology. Real-time transaction notifications, automatic savings features, and spending analytics tools help users maintain better control over their financial health.
Beyond consumer banking, digital lending platforms have transformed how both individuals and businesses access credit. Companies like LendingClub, Prosper, and Kabbage use alternative data sources and sophisticated algorithms to assess creditworthiness, often providing loan decisions in minutes rather than weeks. This is particularly transformative for small businesses and individuals who might not fit traditional lending criteria but are nonetheless creditworthy when evaluated through more nuanced, data-driven approaches.
Investment Democratization: Wealth Management for Everyone

Historically, professional investment advice and portfolio management were services reserved for the wealthy, with high account minimums and substantial advisory fees placing them out of reach for average investors. Fin Tech has democratized investment management through robo-advisors and micro-investing platforms that make sophisticated portfolio strategies accessible to anyone with a smartphone and a few dollars to invest.
Robo-advisors like Betterment, Wealthfront, and similar platforms use algorithms to create and manage diversified investment portfolios based on individual risk tolerance and financial goals. These services charge a fraction of what traditional financial advisors demand, typically around 0.25% annually compared to 1% or more for human advisors. The algorithms continuously rebalance portfolios, harvest tax losses, and adjust allocations as market conditions change, providing professional-grade management at consumer-friendly prices.
Micro-investing apps like Acorns and Stash have taken accessibility even further by eliminating account minimums and allowing users to invest spare change from everyday purchases. These platforms round up transactions to the nearest dollar and automatically invest the difference, making it possible for people who never thought they could afford to invest to begin building wealth gradually. The psychological barrier of needing thousands of dollars to start investing has been completely removed.
Fin Tech platforms have undergone similar democratization. Commission-free trading pioneered by companies like Robinhood has forced the entire brokerage industry to eliminate trading fees, saving investors billions of dollars annually. Real-time market data, research tools, and educational resources that were once exclusive to professional traders are now available to retail investors at no cost. While this democratization has raised important questions about market education and speculative behavior, it represents a fundamental shift in financial inclusion.
Also Read this; 45 Million Won to USD: Essential Insights for Better Financial Planning
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency: Reimagining Money Itself
No discussion of Fin Tech would be complete without addressing blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies, which represent perhaps the most radical reimagining of financial systems in centuries. Bitcoin, Ethereum, and thousands of other digital currencies operate on decentralized networks that eliminate the need for traditional intermediaries like banks and payment processors. While cryptocurrency remains controversial and volatile, the underlying blockchain technology has profound implications for everything from cross-border payments to supply chain management to digital identity verification.
Fin Tech contracts, self-executing agreements coded directly into blockchain networks, could automate countless financial processes that currently require lawyers, escrow services, and other intermediaries. Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms are attempting to recreate traditional financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading using blockchain technology, potentially creating a parallel financial system that operates outside traditional regulatory frameworks and institutional control.
Beyond speculative investment, cryptocurrency is proving particularly valuable for international remittances. Migrant workers sending money home to families in other countries have traditionally faced exorbitant fees and slow processing times through services like Western Union. Cryptocurrency-based remittance services can complete these transfers in minutes at a fraction of the cost, representing real financial relief for some of the world’s most economically vulnerable populations.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Smarter Financial Services

Artificial intelligence and machine learning are the engines driving much of modern Fin Tech innovation. These technologies analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, make predictions, and automate decisions in ways that humans simply cannot match in terms of speed and scale. Financial institutions use AI for fraud detection, credit scoring, customer service, regulatory compliance, and countless other applications that improve efficiency while reducing costs and risks.
Fin Tech detection systems now analyze millions of transactions in real-time, identifying suspicious patterns and blocking fraudulent activity before it impacts consumers. These systems learn continuously, adapting to new fraud techniques as they emerge. The accuracy of AI-driven fraud detection far exceeds traditional rule-based systems, dramatically reducing both false positives that frustrate legitimate customers and false negatives that allow fraud to slip through.
Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by natural language processing provide customer service 24/7, answering questions, resolving issues, and helping users navigate financial products without human intervention. While these systems cannot yet handle every situation, they successfully resolve the majority of routine inquiries, freeing human customer service representatives to focus on complex problems that require empathy and nuanced judgment.
Credit scoring has been revolutionized by machine learning algorithms that consider hundreds or even thousands of data points beyond traditional credit reports. Alternative data sources like utility payment history, education, employment patterns, and even social media activity can provide more accurate assessments of creditworthiness, particularly for individuals with limited traditional credit history. This has the potential to expand credit access while actually reducing default rates.
Insurance Innovation: From Policies to Protection
The insurance industry, long considered one of the most traditional and change-resistant sectors, is being transformed by Fin Tech applications collectively known as InsurTech. These innovations are making insurance more personalized, affordable, and accessible while streamlining everything from policy shopping to claims processing.
Telematics devices and smartphone apps now allow auto insurers to track actual driving behavior, offering discounts to safe drivers based on real-world data rather than demographic assumptions. Similarly, wearable fitness trackers enable health insurers to reward healthy behaviors with lower premiums. This shift toward personalized, behavior-based insurance pricing represents a fundamental change in the insurance model, aligning incentives between insurers and policyholders around risk reduction.
The claims process, historically one of the most frustrating aspects of insurance, has been dramatically improved through technology. Smartphone apps allow policyholders to photograph damage, submit claims, and receive settlement offers in hours or days rather than weeks or months. AI-powered damage assessment can evaluate vehicle or property damage from photos, providing instant estimates that expedite the entire claims process. Blockchain technology is being explored for automating claims through smart contracts that automatically trigger payments when predefined conditions are met.
Regulatory Technology: Compliance in the Digital Age
As financial services become increasingly digital and complex, regulatory compliance has become more challenging and expensive. Regulatory technology, or RegTech, applies Fin Tech solutions to help financial institutions meet their compliance obligations more efficiently. These systems automate reporting, monitor transactions for suspicious activity, and help firms navigate the constantly evolving landscape of financial regulations across multiple jurisdictions.
Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) requirements, which traditionally involved labor-intensive manual processes, can now be largely automated through AI and machine learning. These systems screen customers against watchlists, verify identities, and monitor transactions for patterns indicative of money laundering or other illegal activities. The automation not only reduces costs but also improves accuracy and consistency in compliance efforts.
For financial institutions, RegTech reduces the risk of costly regulatory violations while freeing up human resources to focus on strategic priorities rather than routine compliance tasks. For consumers, these technologies enable faster account opening and more seamless experiences while maintaining the protections that financial regulations provide.
The Future of Fin Tech: Emerging Trends and Challenges
Looking ahead, several trends will shape the continued evolution of financial technology. Open banking initiatives, which require financial institutions to share customer data (with permission) through secure APIs, are enabling new generations of financial applications that aggregate accounts, provide holistic financial advice, and facilitate seamless payments. This data sharing fundamentally challenges the information monopolies that banks have traditionally enjoyed.
Embedded finance, the integration of financial services directly into non-financial platforms and experiences, is making finance increasingly invisible. When you buy insurance at the moment of booking a trip or access a loan at the point of an online purchase, that’s embedded finance at work. This trend will accelerate, making financial services feel less like separate transactions and more like seamless elements of broader experiences.
However, the Fin Tech revolution also faces significant challenges. Cybersecurity threats grow more sophisticated as financial services become more digital, with data breaches potentially exposing millions of consumers to fraud and identity theft. Regulatory frameworks struggle to keep pace with innovation, creating uncertainty for both established institutions and startups. Questions about financial inclusion persist, as those without smartphones or internet access risk being left further behind by an increasingly digital financial system.
Privacy concerns loom large as financial technology companies collect unprecedented amounts of data about our spending, saving, investing, and even physical location. The concentration of this data creates both security risks and questions about how this information might be used beyond its original purpose. Striking the right balance between innovation and consumer protection remains an ongoing challenge for policymakers worldwide.
Conclusion: A Financial Revolution Still Unfolding
The transformation of finance through technology is not a future possibility but a present reality that continues to accelerate and expand. Fin Tech has made financial services more accessible, affordable, and user-friendly while challenging the dominance of traditional institutions that have shaped finance for centuries. From the simple act of splitting a dinner bill through a mobile app to the complex algorithms managing investment portfolios, technology has fundamentally changed how we interact with money.
Yet this revolution is far from complete. The full potential of blockchain, artificial intelligence, and emerging technologies remains largely unrealized. As these tools mature and new innovations emerge, we can expect continued disruption of financial services, with implications that extend far beyond convenience to questions of economic inclusion, financial stability, and the very nature of money itself.
For consumers, the message is clear: financial technology offers unprecedented opportunities to take control of personal finances, access services that were once out of reach, and benefit from competition that drives down costs and improves quality. For traditional financial institutions, adaptation is not optional but essential for survival in an increasingly digital economy. And for society as a whole, the challenge is ensuring that technological progress serves broad prosperity rather than exacerbating existing inequalities or creating new vulnerabilities. The financial future is being written today, one innovation at a time, and the story of Fin Tech is ultimately the story of how we can harness human ingenuity to create a more efficient, inclusive, and equitable financial system for everyone.